Research Projects
Seminar ‘Corpus Linguistics’
Quirin Würschinger, LMU Munich
June 3, 2025
Outline
- Requirements & consulting
- Term papers & research projects
- Topics, research questions & hypotheses
- Interactive: Topic Pitch
- Break (5 min)
- References & citing
- Paper structure & writing tips
- Research areas & examples
- Wrap-up & take-home messages
Term Paper Requirements & Consulting
Term paper submission deadlines
Short papers: 29 August
Long papers: 8 September
Submit your term paper via email by the end of the day.
Term paper consulting
Registration
Register for one of the slots beforehand via mail.
Information required before the meeting
At least one day before the meeting via email.
- research questions and hypotheses
- data and method
- (abstract)
- table of contents
- bibliography
Consulting dates
- 28 July
- 10:00
- 16:00
- 8 August
- 10:00
- 13:00
Zoom meeting
- https://lmu-munich.zoom.us/j/5385530182?pwd=SE5iZDJGQlZ1V3dpN2Q4NW45WjF5Zz09
- Meeting ID: 538 553 0182
- Passcode: 531379
Term Papers & Research Projects
Goal
- Research question with a linguistic focus (+ hypotheses)
- drives the whole project and tells the reader why the study matters
- Empirical study based on observable language use
- collect evidence rather than rely on intuition or arm-chair examples
- Corpus data as the primary evidence base
- pick a corpus that fits your question (size, genre, time span)
- Corpus-linguistic methods for analysis
- e.g. frequency, collocations, distribution across speakers or texts
What is a topic?
- a more general account of what your are interested in
- a vague formulation of your project
- the area and discipline you are working in
What is a good topic?
- is not too general but also not too specific
- should have further relevance for linguistics
- includes new aspects based on the state of the art
- is interesting and doable
- is based on previous knowledge and/or observations
- allows for a number of research questions
Title
- is the business card of your paper/thesis
- must be informative and explicit
- must have a reasonable link to the content
- must not raise unmet expectations
- it’s often good to use a subtitle
Research Questions & Hypotheses
- How to find RQs?
- from previous literature
- by coming across a suggestion for desiderata / unanswered questions
- by replicating someone else’s work
- by identifying a gap, i.e. something that has not yet been asked
- from observation
- from own empirical findings within the study
- from previous literature
Key Questions
- Which topic do I want to work on?
- Is it broad enough to be interesting?
- Is it narrow enough to be doable?
- Which research question do I want to work on?
- Does it have a strong enough linguistic focus?
- What are my hypotheses?
- What do I expect the outcome of my study to be?
- Why do I expect these results (e.g. previous studies, theoretical models)?
- How does my research question relate to previous work?
- Where lies the contribution of my project?
- Which data could I use to study my research question?
- Which methods could I use to test my hypotheses?
Interactive: Topic Pitch (Think–Pair–Share)
Goal: formulate a concise, doable topic and receive quick peer feedback
Steps:
- write one-sentence topic idea (1 min)
- pair up and exchange ideas (90 s each)
- give one suggestion or question to your partner
- be ready to share a highlight in plenary
Break
- 5-minute break – stretch, grab water, come back refreshed
Finding References
- Libraries
- LMU: OPAC & Databases (e.g., LLBA, MLA)
- BSB: OPAC
- Web
- Google Scholar, OpenAlex, Semantic Scholar, Connected Papers
- I cannot recommend using the ‘Dark Web’.
- e.g., LibGen, SciHub
- Research network platforms
- academia.edu, ResearchGate
- ‘Schneeballprinzip’ (snowballing)
- Check references of relevant papers.
- AI-assisted services
- e.g., elicit.org
Citing References
- Style Guides
- Stilblatt Anglistik LMU
- Chicago Author-Date Style
- Unified Style Sheet for Linguistics
- APA
- In-text citations
- Use author-date format, e.g., “Here’s an interesting quote.” (Schmid 2020: 420)
- Bibliography
- Must be consistent and follow a style guide.
- Must only contain sources you have cited.
Managing References
Structure of a Term Paper
Overview
- Introduction
- Theoretical Background
- Data
- Method
- Results
- Discussion
- Conclusion
Introduction
Your introduction should:
- Grab the reader’s attention and introduce the topic.
- Provide the necessary context and establish the relevance of the research.
- Clearly state your research question and/or hypothesis.
- Provide a brief roadmap or summary of what the paper will cover.
Theoretical Background
Your theoretical background should:
- Provide a detailed review of the existing literature.
- Highlight the key theories and findings of previous studies.
- Show how previous work relates to your own research.
- Clearly define any key terms and concepts.
Data & Method
Your data and method section should explain:
- Data: What data you are analyzing (source, selection criteria, characteristics).
- Corpus: For corpus papers, provide a detailed description of your corpus.
- Method: The methods used to analyze your data.
- Tools: Any specific techniques, procedures, or software you used.
Results & Discussion
- Results:
- Present your findings clearly and concisely, using tables or graphs where appropriate.
- Ensure your results directly address your research question or hypothesis.
- Discussion:
- Interpret your results in the context of the existing literature.
- Discuss whether the results support your hypothesis and what their broader implications are.
- Acknowledge any limitations of your study and suggest areas for future research.
Conclusion
Your conclusion should:
- Start with a strong summary of your key findings.
- Reiterate the answer to your initial research question.
- Discuss the broader implications of your work for linguistics.
- Acknowledge any limitations of your study.
- Suggest concrete avenues for future research.
Style and Readability
- Be concrete and explain.
- Aim for a neutral, scientific, academic style.
- Aim for understandable, precise, clear formulations.
- Use topic sentences and examples.
- Put the main thing in the main clause.
- Use active instead of passive; use verbs instead of nouns.
Tools for Writing
- Dictionaries: linguee, dict.cc
- Thesauri: thesaurus.com
- Collocations: ozdic.com, netspeak.org
- Spelling & Grammar
- AI-based tools
- Phrasebanks
Research Areas & Topics
Some broad areas you could focus on.
- Linguistic Variation: How does language vary between speakers, text types, or geographical regions?
- speaker variation: e.g., tag questions across age, gender, social class
- text type/register variation: e.g., modal verb frequency in academic vs. fiction
- geographical variation: e.g., fall vs. autumn
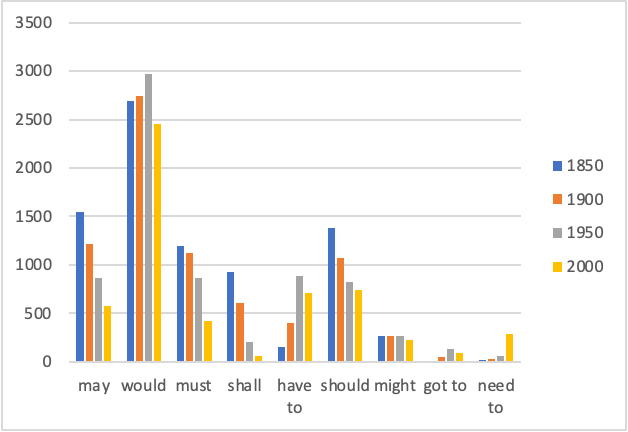
- Language Change: How does language change over time?
- lexical change: rise of neologisms such as hangry
- semantic change: shift in collocates, cf. gay
- grammatical change: diffusion of constructions along an S-curve (e.g. going to future)
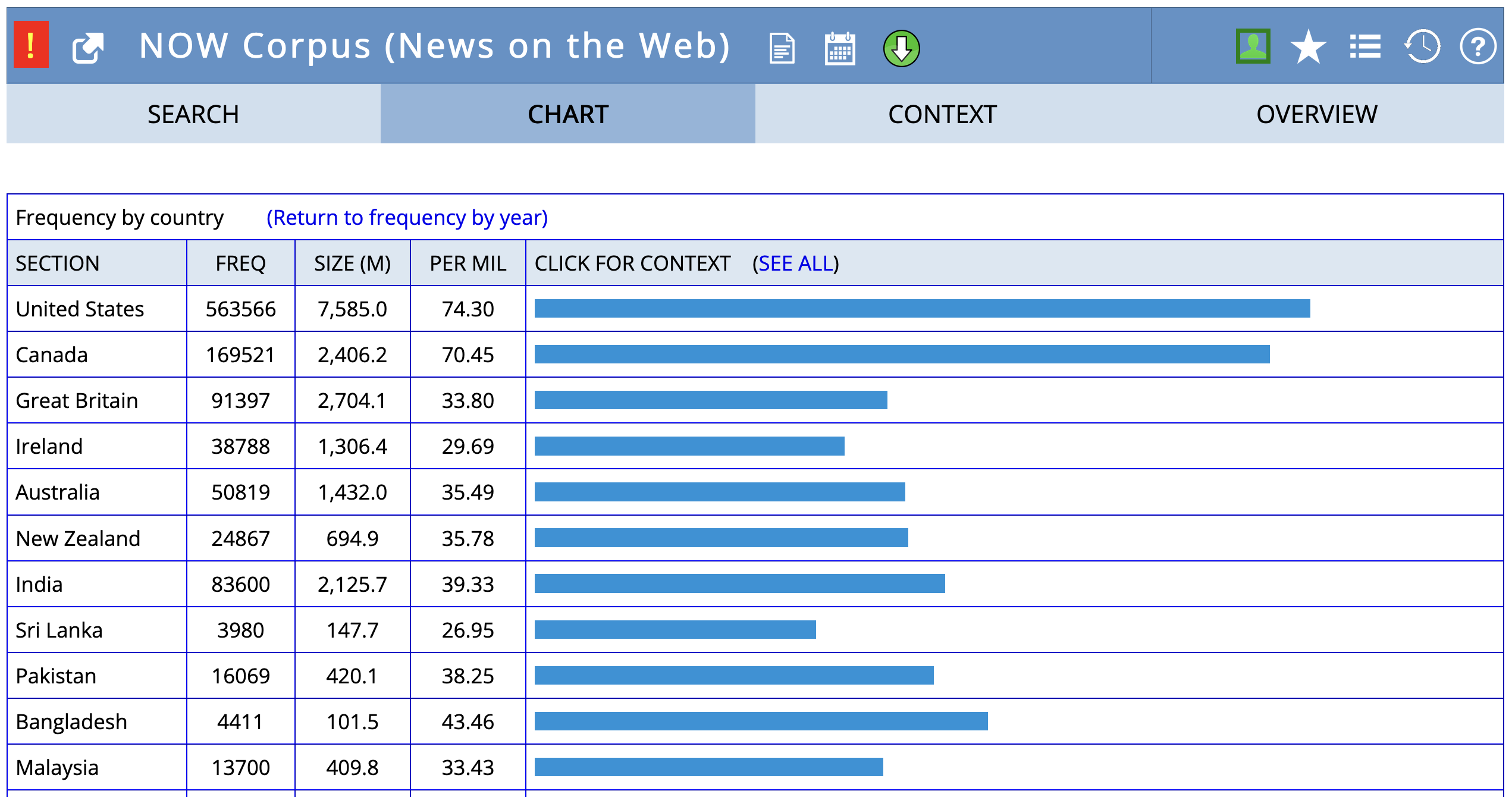
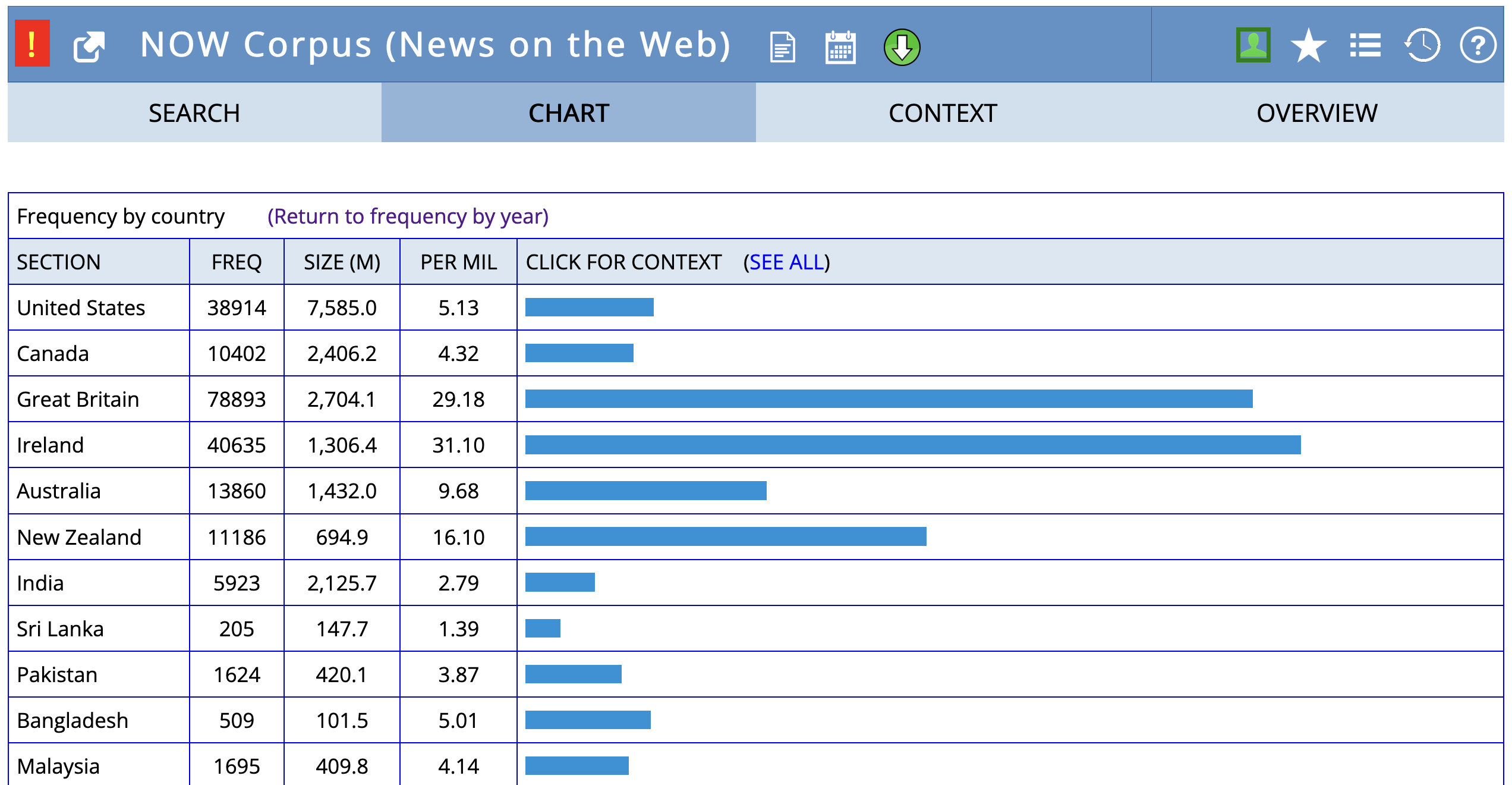
Example: Geographical Variation
Frequency of fall vs. autumn by country in the NOW corpus.
fall
autumn
Example: Language Change
Theoretical Frameworks
Your research can be grounded in various theoretical frameworks:
- Usage-based approaches: How do patterns of language use shape grammar and meaning?
- S-Curve Model: How do linguistic innovations spread through a community?
- Entrenchment-and-Conventionalization Model: How do novel expressions become fixed conventions?
- Distributional Hypothesis: How can we understand the meaning of a word by looking at the contexts in which it appears?
Domains of Language
Lexis
- The study of vocabulary, including its innovation and diffusion.
- Neologisms are new words or expressions.
- Can you think of recent examples?
- staycation, glamping, hangry, cringe, social distancing, medfluencer
- These can be investigated by looking at their frequency over time (e.g., in the English Trends corpus) or their distribution across text types (e.g., in enTenTen).
Morphology
- The study of word formation and internal structure.
- Clipping is a common word-formation process where a word is shortened.
- For example, brother becomes bro, or refrigerator becomes fridge.
- Research questions could explore:
- Do source words and clipped forms differ in meaning?
- How does their usage vary across text types or over time?
- A corpus-based analysis could compare their frequency, collocations, and word sketches.
Syntax & Semantics
- Syntax: The study of sentence structure.
- An example topic is the study of a specific grammatical construction, like the the N BE that construction (e.g., “The problem is that…”).
- Semantics: The study of meaning.
- An example topic is semantic change, where you could investigate how the meaning of a word has evolved over time by analysing its changing collocates.
Data, Corpora & Methods
- Corpora
- Sketch Engine: Gutenberg English 2020, EEBO, enTenTen20, English Trends
- english-corpora.org: COHA, COCA, NOW
- Methods
- Frequency
- Collocations
- Word Sketches
Further Reading
See Stefanowitsch (2020) for further examples and case studies.
- Stefanowitsch, Anatol. 2020. Corpus linguistics: A guide to the methodology. Language Science Press.
Workshop: Mini Research-Design (Group)
- Group task: draft a mini study plan for one research area and add one slide to the shared deck: https://1drv.ms/p/c/9a2ec97d593520f9/EUu0cQtCO1pMnlyH0FZKnRMBFWa2hCajBPKjPBhkbnPZog
- Template (fill on your slide):
- Research question
- Hypothesis (optional)
- Corpus / data
- Method(s)
- Expected finding(s)
- During plenary (last 8 min):
- each group presents their slide (≈ 60 s)
- audience notes one idea or question
- quick Q&A if time permits
Summary
- A strong research question is the compass of your study – keep asking why and how.
- Map the literature first, then locate your own contribution.
- Let the research question choose the corpus, not the other way round.
- Plan methods early, keep them transparent and replicable.
- Write clearly: main point in main clause, verbs over nouns.
- Today’s pitch and design drafts are seeds – Keep working towards your term paper!